CloudFlare DDOS Attack, the largest Distributed Denial of Service Attack in the world! NTP based 400 Gbs DDOS Attack
Security company CloudFlare said Monday that a customer running on its platform was hit with a massive DDOS attack and that affected service in all the Europe, even in some of its US infrastructure.
“It was a very large DDoS targeting a CloudFlare customer,” Matthew Prince, CEO of Cloudflare told SecurityWeek. “We’re still gathering the log data to get exact numbers but know it was well over 300Gbps and likely over 400Gbps”, said Matthew Prince.
“The method was NTP reflection, which is quickly replacing DNS reflection as the source of the largest attacks”, said Matthew Prince.
CloudFlare did not mentioned the name of the customer that was targeted in this particular attack.The security firm is usually quite transparent about its operations.
What is DDOS Attack?
Distributed Denial of Service attacks were common in the last months. These affected sites like WordPress or Spamhaus and even led to the destabilization of the virtual currency Bitcoin. The Spamhaus DDoS attack was so great that it affected the speed of the Internet globally.
DDoS attacks are used to overwhelm servers with requests. All requests are directed to the same place on the server and thus there are no answers for new server requests. The Distributed Denial of Service ( DDOS ) is one of the best weapons of the hackers, because, until now, nearly every big site had been a victim of this attack.
What is ( Network Time Protocol ) NTP DDOS attack? How to understand it better.
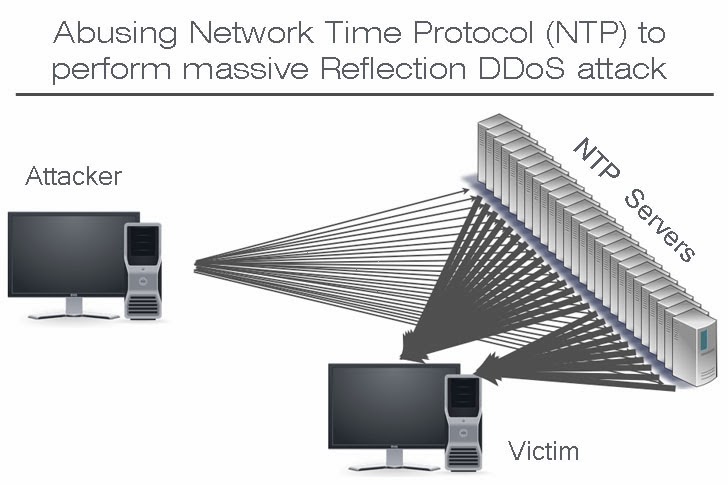
The NTP method first began to appear late last year. To bring down a server such as one running “League of Legends,” the attackers trick NTP servers into thinking they’ve been queried by the “League of Legends” server.
The NTP servers, thinking they’re responding to a legitimate query, message the “League of Legends” server, overloading it with as many as 100 gigabits per second (Gbps). That’s large even for a DDoS attack.
In this way, one small request to an NTP server can generate an enormous response capable of taking down even high-capacity websites.
Source – schneier.com

